Vector vs. Raster: Understanding Image Formats

In the digital world, images are the visual language that communicates ideas, captures memories, and brings designs to life. But not all images are created equal. Whether you're a graphic designer crafting a logo, a photographer preserving a moment, or a web developer creating stunning visuals, understanding the fundamental differences between vector and raster images is crucial to achieving the best results.
What are Raster Images?
Raster images are the most common type of digital images you encounter every day. Composed of tiny squares called pixels, these images are like intricate mosaics where each pixel represents a specific color and position. Think of digital photographs, web graphics, and most images you see online – they're typically raster images.
Understanding Pixels and Resolution
At the core of raster images are pixels – the smallest units of a digital image. Imagine a grid where each square is filled with a specific color. The more pixels in this grid, the higher the resolution and the more detailed the image appears. Image resolution is typically measured in dots per inch (DPI), with 72 DPI providing crisp screen displays and 300 DPI delivering high-quality prints. When you zoom in on a raster image, you'll see these individual pixels become more apparent, which is why these images have limitations in scaling.
Common Raster Image Formats
The digital world offers several raster image formats, each with unique characteristics. JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is widely used for photographs, offering lossy compression that reduces file size while maintaining reasonable image quality. It's ideal for web use and digital photography. PNG (Portable Network Graphics) stands out for its ability to support transparency and provide lossless compression, making it perfect for web graphics and logos with complex backgrounds. GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) is known for supporting simple animations and using a limited color palette, which makes it popular for memes and basic web animations.
Pros and Cons of Raster Images
Raster images excel in certain areas while presenting challenges in others. Their strength lies in representing complex color gradients and capturing photorealistic details. They are perfect for photography and web graphics that require intricate color variations. However, they come with significant limitations. Raster images are resolution-dependent, meaning they lose quality when resized. Enlarging a raster image reveals individual pixels, creating a blocky, unprofessional appearance. Additionally, high-resolution raster images can result in large file sizes, which can slow down websites and consume significant storage space.
When to Use Raster Images
Professionals choose raster images in specific scenarios where detailed, color-rich representations are crucial. Photographers rely on raster formats to capture the nuanced colors and textures of their subjects. Web designers use raster graphics for complex illustrations, social media content, and detailed web graphics. Digital artists create intricate illustrations that leverage the pixel-based precision of raster images.
What are Vector Images?
Unlike raster images, vector images are created using mathematical formulas and geometric primitives like points, lines, and curves. Instead of pixels, vectors use precise coordinates and algorithms to define shapes and colors.
Mathematical Precision and Scalability
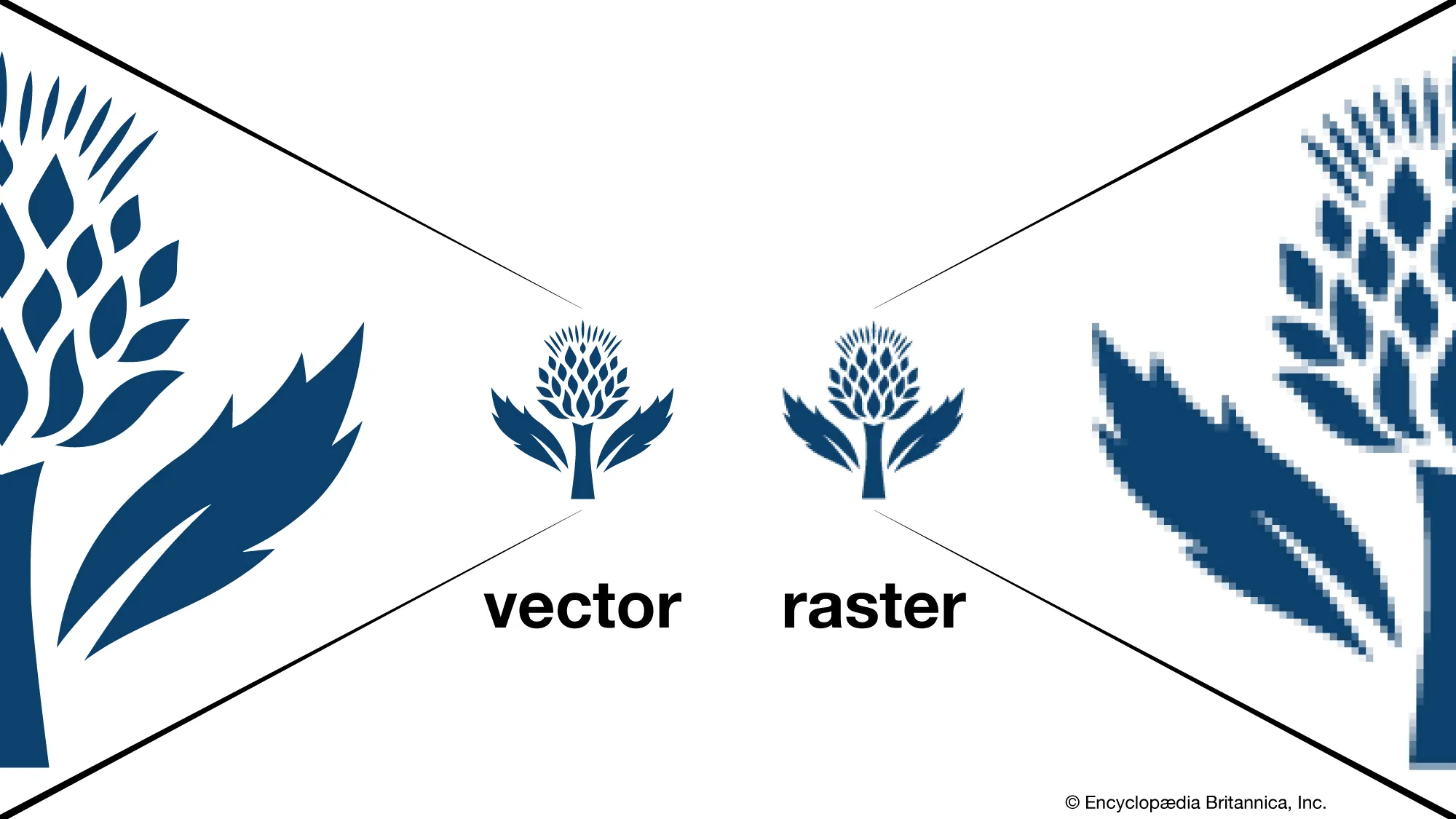
Vector graphics are defined by mathematical equations, which means they can be scaled infinitely without losing quality. Imagine drawing a line – no matter how much you zoom in or out, the line remains crisp and clean. This mathematical foundation allows vector images to maintain perfect clarity at any size, from a small icon to a massive billboard.
Common Vector Image Formats
The vector world offers several specialized formats for different use cases. SVG (Scalable Vector Graphics) is an XML-based format that's web-friendly and incredibly lightweight. It allows for easy customization and is perfect for responsive web design. Adobe Illustrator's native AI format provides professional-grade vector editing capabilities for complex design projects. EPS (Encapsulated PostScript) remains a traditional format widely used in professional printing workflows, offering compatibility and precision.
Pros and Cons of Vector Images
Vector images bring remarkable advantages to digital design. Their infinite scalability means a logo can be used on a business card or a massive billboard without any loss of quality. Vector files are typically smaller than equivalent raster images, making them efficient for storage and transmission. They're also incredibly easy to edit, with each element existing as a separate, manipulatable object. However, vector graphics aren't without limitations. They struggle to create photorealistic images and cannot represent complex color gradients with the same nuance as raster images. Creating vector graphics requires specialized software and a different design approach compared to traditional pixel-based artwork.
When to Use Vector Images
Graphic designers and brands turn to vector images for specific design needs. Logos and branding materials benefit immensely from vector formats, ensuring consistent quality across various applications. Icons, illustrations, and technical diagrams shine in vector format. Large-format printing, such as signage and promotional materials, relies on vector graphics to maintain crisp, clean lines at any size. Motion graphics and animations also leverage vector images for their scalability and precision.
Vector vs. Raster: Key Differences
| Characteristic | Vector Images | Raster Images |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Infinitely scalable | Limited by original resolution |
| File Size | Typically smaller | Can be large, especially high-resolution |
| Detail Level | Crisp geometric shapes | Photorealistic, pixel-dependent |
| Best Use Cases | Logos, illustrations | Photography, complex graphics |
| Editing Flexibility | Easily editable | Limited editing without quality loss |
Converting Between Vector and Raster
Converting between these formats isn't always straightforward:
Raster to Vector Conversion
- Tracing software can convert raster to vector
- Best for simple, high-contrast images
- Loss of subtle details is common
- AI-powered tools are improving conversion accuracy
Vector to Raster Conversion
- Simple process of exporting at desired resolution
- Retain original vector file for future edits
- Choose appropriate resolution for intended use
Top Tools for Vector and Raster Conversions
Converting between vector and raster formats can be challenging, but several powerful tools make the process more accessible for designers and professionals. Each tool offers unique features to help you transform your images while preserving as much quality as possible.
Raster to Vector Conversion Tools
Adobe Illustrator stands out as the professional standard for vector conversions. Its Image Trace feature allows designers to convert raster images into editable vector graphics with impressive precision. While powerful, it requires a subscription to Adobe Creative Cloud, which can be costly for individual users.
Inkscape provides a free, open-source alternative for vector conversions. This comprehensive vector graphics software offers trace capabilities that work well for simple to moderately complex images. It's particularly useful for designers on a budget who need reliable conversion tools.
Vector Magic represents a specialized online service dedicated to raster-to-vector conversions. Their advanced algorithms can handle intricate images with remarkable accuracy. They offer both online and desktop versions, with pricing options for occasional users and professionals who need frequent conversions.
Vector to Raster Conversion Tools
Adobe Photoshop remains the gold standard for converting vector graphics to high-quality raster images. Its export options allow designers to set precise resolution and file format specifications, ensuring optimal image quality for different use cases.
Affinity Designer provides a more affordable alternative to Adobe's suite, offering robust vector to raster conversion capabilities. It's particularly popular among freelancers and small design studios looking for professional-grade software at a lower price point.
Online Conversion Tools
For those seeking quick, no-installation solutions, several online platforms offer convenient conversion services:
Convertio supports multiple file format conversions, including vector and raster transformations. It's user-friendly and doesn't require software installation, making it ideal for occasional users.
CloudConvert offers comprehensive file conversion services, supporting a wide range of vector and raster formats. Their platform ensures secure file handling and provides high-quality conversions for various image types.
Considerations When Converting Images
While these tools are powerful, it's important to manage expectations. Raster to vector conversions can never perfectly recreate the original image, especially for complex photographic images. The best results come from:
- Using high-contrast source images
- Choosing appropriate trace settings
- Understanding the limitations of conversion algorithms
- Manually refining the converted image
Professional designers often find that manual tracing or recreating the image from scratch yields the most accurate results, particularly for intricate or nuanced designs.
Ironov.ai and Image Editing
At Ironov.ai, we understand the critical importance of visual identity in today's competitive business landscape. Our AI-powered platform specializes in creating stunning, professional logo designs and comprehensive brand identities. We recognize that the right image format can make or break a brand's visual communication. That's why our logo designs are created as vector graphics, ensuring maximum flexibility and quality across various applications.
Our AI technology generates unique, custom logo designs that can be instantly downloaded in multiple formats. Whether you need a crisp SVG for web use, a high-resolution AI file for print materials, or a versatile PNG for digital platforms, Ironov.ai provides the perfect solution. We transform your brand vision into a scalable, professional visual identity that looks impeccable from a small business card to a large billboard.